The nuclear fuel cycle
Introduction
The nuclear fuel cycle is the set of processes to condition fertile and fissile materials to produce energy in a nuclear reactor and subsequently reprocess and recycle, or store them, safely safeguarding the resulting radioactive waste.
The fuel cycle begins with the extraction of uranium ore, going through its milling, concentration, conversion, enrichment, fuel irradiation in the reactor, and the steps associated with the selected spent fuel disposal strategy.
The nuclear fuel cycle can be divided into two categories, the open cycle and the closed cycle; the main difference being that the irradiated fuel is not reprocessed and recycled in the open cycle. As can be seen in Figure 1, in the open cycle, the fuel once it leaves the nuclear reactor is temporarily stored, either in spent fuel pools and/or in containers or in concrete vaults; these last two known as dry storage methods. Subsequently, the spent fuel is properly conditioned and definitively disposed of in a permanent repository, such as a Deep Geological Storage.
All the stages that are carried out before the irradiation or utilization of the fuel in a nuclear reactor, that is: mining and milling, conversion, enrichment, and fuel fabrication, is known as the front-end of the nuclear fuel cycle, which is the subject of this module.
Figure 1. Nuclear fuel cycle.
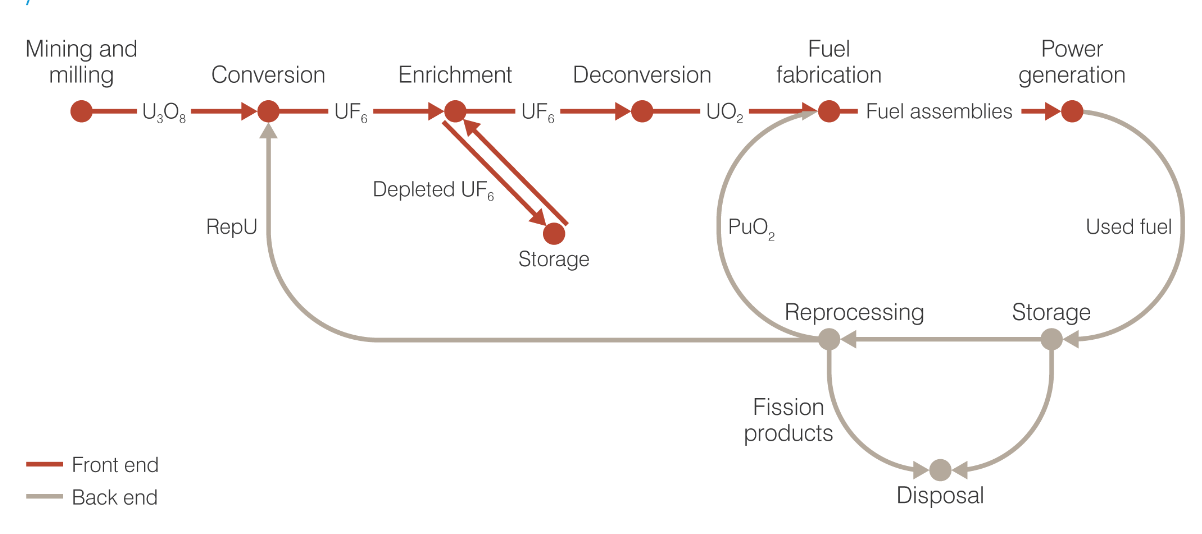
Fuente: World Nuclear Association Image Library (https://www.world-nuclear.org/gallery/the-world-nuclear-fuel-report-expanded-summary/the-nuclear-fuel-cycle.aspx)
Objectives
The student:
- Describe the nuclear fuel cycle.
- Recognize the difference between the open and closed loop.
- List the different stages of the front-end.
- Analyze the basic characteristics of each stage of the front-end.
- Select information about the countries with facilities associated with each stage of the front-end.
- Apply the method to calculate the masses of the materials associated with each stage of the front-end.
Module evaluation form
- The student will solve a questionnaire by topic and apply a case study.

